WAN - collection of computers spread over a wide geographical area. Communication may be via microwave, satellite link or telephone line (typically transitory)
Communication links
- Twisted pair (copper cable) -> telephone line (analogue) - cheap, slow transmission rates, electronic interference
- Coaxial cable - high quality, well insulated, high speeds, more accurate
- Fibre optic cable - pulses of light sent in digital form
- Microwave - cannot be more than 30 miles apart due to Earth's curvature
- Communications satellite - geosynchronous orbit 22000 miles above the Earth
Types of coaxial cable
- Baseband
- carries one signal at a time
- signals can travel very fast but can only be sent over short distances (booster equipment required after 1000 feet)
- Broadband e.g. ISDN -> broadband digital communications technology
- can carry multiple signals on a fixed carrier wave
- faster transmission rates than with a modem and telephone line
- enables transmission of voice, video and computer data simultaneously -> videoconferencing
Synchronous data transmission e.g. LAN
- timing signals synchronise the transmission at the sending and receiving end
- no need for start and stop bits for each character (only at beginning and end of whole block)
- higher transfer rates (but may be more errors)
Multiplexor - combines more than one input signal into a stream of data that can be transmitted over a communication channel
- increase efficiently of communication and saves cost of individual channels
Demultiplexor - separates the single stream of data into separate components at the receiving end
Time-division multiplexing - transmission time split up into tiny time-slices
- each user can transmit a small amount of data in turn
- high bandwidth -> thousands of users can transmit digital data/have telephone conversations apparently simultaneously down a single high speed wire
Circuit switching e.g. public telephone system
- set fixed message path for the duration of the call by operating switches in all exchanges involved in the path
- electrical interference produced
Packet switching e.g. Internet
- messages are divided up into packets (fixed length blocks of data)
- packets contain:
- data
- source and destination address
- packet sequence number (so that the whole message can be correctly reassembled)
- checksum for error checking
- packets may be sent along different routes and are reassembled by the packet switching system (PSS) at the receiving end
- computers in PSS can perform error checking -> request transmission of packets found to be in error or perform error correction
- each user requires a network user identity
Virtual circuit - temporary 'dedicated' pathway between two points on a PSS -> bandwidth allocated for a specific transmission pathway
Advantages of packet switching:-
- more efficient use of lines
- cost depends on number of packets sent, not distance, so all data can be transmitted at local call rates
- less likely to be affected by network failure because of multiple routes available to transmit data packets
- better security (data less likely to be intercepted because the packets may be sent along different routes or interleaved with other unrelated packets)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- type of packet-switching system which can support a wide range of different data types (e.g. computer data, voice, fax, CD-quality audio, real-time video)
- packets referred to as cells
- digital lines -> noise-free and error-free communication -> high transmission rates
Standard (network) protocols - in order for two computers on a network to communicate successfully, they must share a common set of rules about how to communicate
- how to interpret signals
- how to identify 'oneself' and other computers on a network
- how to initiate and end networked communications
Protocol stack - provides software that enables computers to communicate across a network
e.g. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
- protocol governing the transmission of data
- data is divided into packets to which addressing information, error correction code and identification are added
- the packets travel to their destination over the network and the receiving PC checks for mistakes and pieces the data together in the right order
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model
- Application Layer - initiates or accepts a request
- Presentation Layer - adds formatting, display and encryption information
- Session Layer - adds traffic-flow control information
- Transport Layer - adds error-handling information
- Network Layer - adds sequencing and address information
- Data Link Layer - adds error-checking information and formats data for physical transmission
- Physical Layer - sends data as a bit stream
Local Area Network
Network topology
- refers to the physical layout of computers, cables and other resources and to how these components communicate with each other
- has an impact on a network's performance and growth
Bus network
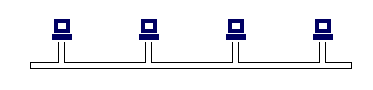
- all components are connected via a backbone (a single cable segment connecting all the computers in a line)
- entire network will be brought down by a single cable break
- terminator at the end of the line absorbs all signals that reach it to clear the network for new communication
- data is sent in packets across the network and received by all connected computers; only the computer with the packet destination address accepts the data
- only one computer can send information at a time
- Ethernet uses a collision system - carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA-CD) - if transmitted messages collide, both stations abort and wait a random time period before trying again
- network performance degrades under heavy load
Ring network
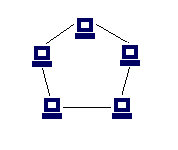
- signals travel in one direction only
- fast topology
- if one computer fails, the whole network will go down
Token passing
- a small packet called a token is passed around the ring to each computer in turn
- to send information, a computer modifies the token, adds address information and sends it down the ring
- information travels around the ring until it reaches its destination or returns to the sender
- when a packet is received by the destination computer, it returns a message to the sender indicating its arrival
Star topology
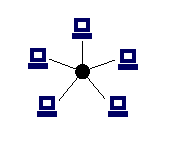
- computers connected by cable segments to a central hub
- a signal sent from a computer is received by the hub and retransmitted down every other cable segment to all other computers on the network
- only the computer the signal is addressed to acts upon the data
- if one computer fails, the others are unaffected
- if the hub goes down, the whole network goes down
Ethernet - network architecture with several different implementations using different types of cable
Segmentation - networks can be segmented to reduce traffic on each segment by inserting a bridge or router between each network segment -> better network performance
Server-based network e.g. Novell's NetWare
- used when there are more than 3 or 4 computers on a network (can support hundreds of users)
- client devices send requests for service (e.g. printing, retrieval of data) to specific server devices
- central backing store available to all users
- software and data centrally held and distributed to clients as they request them
- some processing tasks are performed by the desktop computer and others handled by the file server
- servers provide network with more speed and power but add expense and complication
- servers may be physically located in a secure office
- user IDs and passwords can be controlled by the central computer
- backup facilities are centralised
- if the central facility goes down, all users are affected
Peer-to-peer network e.g. Microsoft Windows 98
- suitable for a small company (under 10 computers) which does not need the power and speed of client-server architecture
- data can be easily accessed from any computer
- each workstation can communicate directly with every other workstation on the network without going through a server
- appropriate when the network users mostly do their own work but occasionally need to share data or communicate with each other
- if a user wishes to retrieve data from a workstation that is switched off, the data cannot be retrieved
- storage facilities are distributed throughout the network
- copies of software may be held on individual machines
- security is not centrally controlled
- backup is the responsibility of individual computer users
- easy and cheap to set up and requires no special network OS
Wide Area Network
Dial-up networking
- user pays for the amount of time spent using the telephone link
- less expensive
- more appropriate for low-volume applications requiring only occasional transmission
Dedicated/leased line
- line is continually available for transmission and the user pays a flat rate for total access to the line
- transmit data at higher speeds
- more appropriate for high volume transmission
Value-added network (VAN)
- private, multipath, data-only, third-party managed network
- used by multiple organisations
- may use ISDN lines, satellite links etc.
- set up by a firm in charge of managing the network
- subscribers pay a subscription fee and for data transmission time
- cost of using the network shared among many users
- subscribers do not have to invest in network equipment or perform their own error checking, routing and protocol conversion
Electronic data interchange (EDI)
- e.g. transmitting A level results to schools using BT's CampusConnect
- virtually instantaneous electronic transmission of business data from one firm's computerised information to that of another firm
- increases accuracy and eliminates delays
Modem
- converts digital signal received from a computer into an analogue signal that can be sent along ordinary telephone lines, and back to digital at the other end
- speed measured in bits per second e.g. 56K bps
- parameters must be specified when a modem is installed:
- the telephone number of the ISP
- baud rate of modem
- number of data bits per block
- number of stop bits
- whether odd or even parity is used
ISDN line - requires a network adapter and a network termination device (no modem required)
Cable modems - employ broadband transmission across regular cable television wires
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ASDL) - offers Internet connection up to 30 times faster than dial-up modems still using traditional copper wires but allocating more bandwidth to the data flow from the ISP to the PC than is allocated from the PC to the ISP
Internetwork
- created when two or more independent networks are connected but continue to function separately e.g. Internet
- in larger networks it is common to supply multiple paths through the network to provide fault tolerance
Bridge
- device that connects networks using the same communications protocols
- cannot handle multiple paths for data
Router
- can route packets of the same protocol (e.g. TCP/IP) over networks with dissimilar architectures (e.g. Ethernet to token ring)
- receives transmitted messages and forwards them to their correct destinations over the most efficient available route
- used to form complex networks with multiple paths between network segments (subnets) -> each subnet and each node on each subnet is assigned a network address
Gateway
- device that connects networks with different architectures and different protocols
- when packets arrive at a gateway, the software strips all networking information from the packet, leaving only the raw data
- gateway translates the data into the new format and sends it on using the networking protocols of the destination system
The Internet
Internet backbone - major Internet communications links maintained by network service providers (NSPs)
World Wide Web
- part of the Internet which allows people to view information stored on participating computers
- consists of pages that contain information on a particular topic and links to other Web pages which may be stored on other computers in different countries
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- provides users with a connection to the Internet and the software needed to navigate
- routes data between computers and Internet backbone
On-line Service Provider - provides users with access to the Internet and its own private network of services
Usenet newsgroups - different newsgroup devoted to specific areas or interest
Email
- send a message anywhere in the world for the price of a local call (cheaper than fax or telephone for long distances)
- attach files (e.g. documents, photographs)
- send the same letter to a group of people simultaneously
- much quicker than mail
- helps effective communication (rules of how to set out a letter don't apply)
- you will be automatically notified if the message doesn't reach the address
- pick up your email from anywhere in the world
Telnet - software program that allows users to connect to a remote computer via the Internet and use the programs on that computer
Disadvantages of email:-
- viruses can be spread in email attachments
- junk mail can be a problem
- direct and informal -> easy to offend people
- can be depressing if overloaded with emails
Web browser - software used to view and download Web pages
Facilities include:-
- bookmark pages for quick reference later
- save most recently visited pages for viewing off-line
- browse back and forward through most recently viewed pages
- play video clips and sounds if appropriate plug-in software is installed
- download files to a local hard disk
- fill in an online form and submit it via email
- netcasting - have pages pushed at you rather than requesting them
- keep a history of pages visited within a specified period
Search engine - enables users to search the contents of millions of Web pages simultaneously
Java applets - small Java programs with the extension .class, which can be executed though Web browsers
Java script - allows fast creation of Web page events
- creates interaction between the user and the Web page
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) - programming language behind every Web page, controlling how the text and graphics are displayed
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - used to download files from the Web or upload pages to a Web site
On-line banking e.g. Smile (on-line bank with no branch network to support customers)
- four times cheaper to operate than telephone banking and 10 times cheaper than high street banking
- fewer high street banks, less office space (fewer overheads), fewer staff
Online shopping
- save on overheads
- 'virtual shop' can have more stock
- 'Just In Time' delivery from suppliers
- list of customers, purchases etc. -> valuable market research tool
- customers can shop at any hour of the day
- customers can hear snatches of music before they buy it
- no jostling crowds
e.g. Tesco for weekly shopping
- save customer time once list initially set up
- £5 charge includes delivery (delivery day confirmed, not time)
Internet registry - to register a domain name (e.g. Nominet)
Cybersquatting - speculating domain names in order to try to earn a profit by selling the names they have registered
Digital certificate
- used to prevent others from viewing incoming mail
- to send an encrypted message you must know the receiver's public key and how to use it
- receiver user private key to decrypt massage
- Outlook express can automatically send your public key with outgoing emails
Digital signature
- authenticates the sender, proves that the message has not been tampered with and prevents the sender from denying having sent it
- mathematical summary (hash code) of document generated and appended to document, transmitted with it and checked at the receiving end. The slightest difference to the document will not generate the same hash code
- a programmer signs a program by attaching their digital signature; programs which have a digital signature are therefore less likely to contain viruses
Encryption
- the scrambling of data so that it becomes very difficult to unscramble and interpret
- performed using cryptographic algorithm (public) and key (private)
- longer key -> greater keyspace (range of possible values)
- used to make it unlikely that ciphertext (scrambled data) could be broken within the period of time during which the contents should remain secret
Decryption - unscrambling ciphertext back to the original plaintext
Strong encryption - implies it would effectively be impossible to find the key within the effective lifetime of the secret
- limits ability of governments to monitor messages by suspected terrorists
- some governments would like to ban it unless a back door is made available to Law Enforcement or a decryption key is lodged with a Trusted Third Party (TTP)
Weak encryption - implies that the key could be found with a realistic amount of processing capacity and a reasonable amount of time
Factoring - attempting to find the two prime factors of a product (used in encryption)
Firewall - mechanism for protecting a corporate network from external communications systems e.g. Internet
- consists of a computer containing two network interface cards (NICs) and running a special firewall program
- one NIC is connected to the company's LAN and the other is connected to the Internet
- computer acts as a barrier through which all information passing between the two networks must travel
- firewall software analyses each packet of information and rejects it if it does not confirm to a preconfigured rule
Viruses e.g. Melissa (1999 macro virus) - mailed itself as attachment to first 50 addresses in Outlook Express Address Book
Blocking software e.g. Net Nanny and Surf Watch
- software censors unsuitable material to combat the dangers to children


